Lemmiwinks: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
Each ECU code stores this adaptation channel data in different RAM |
Each ECU code stores this adaptation channel data in different RAM |
||
locations. To make this method work with any ECU one runs through the |
locations. To make this method work with any ECU one runs through the |
||
following steps: |
following steps: |
||
# Establish communications with the ECU using KWP2000 mode |
|||
# Read data directly from serial eeprom (since read access is allowed) |
|||
# Search for this data in the ECU's RAM |
|||
adaptation channel settings to the RAM location; 5) Cycle ignition key |
|||
# Write the new adaptation channel settings to the RAM location |
|||
# Cycle ignition key to have ECU transfer the new settings into the serial eeprom. |
|||
The KWP2000 protocol is not as reliable as the VAG protocol. Some cars |
The KWP2000 protocol is not as reliable as the VAG protocol. Some cars |
||
Revision as of 05:52, 2 August 2006
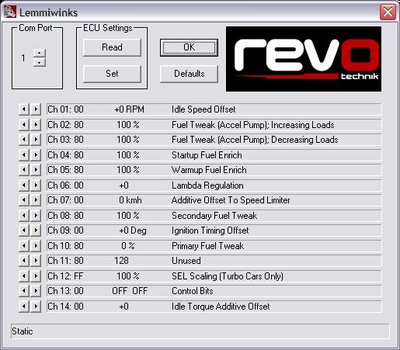
Channel summary
| 01 | Idle Speed Offset | Adjust idle RPM level | Increase/decrease idle (RPM) |
| 02 | Fuel Tweak (Accel Pump) - Increasing Loads | Fuel trim tweak while load is rapidly increasing | Add/remove fuel (%) |
| 03 | Fuel Tweak (Accel Pump) - Decreasing Loads | Fuel trim tweak while load is rapidly decreasing | Add/remove fuel (%) |
| 04 | Start Up Fuel Enrich | Fuel trim during engine start | Add/remove fuel (%) |
| 05 | Warm Up fuel Enrich | Fuel trim during engine warmup | Add/remove fuel (%) |
| 06 | Lambda Regulation | Controls narrow band 02 cycle time | Increase/decrease cycle time |
| 07 | Additive Offset To Speed Limiter | Speed limiter | Increase/decrease speed limiter (km/hr) |
| 08 | Secondary Fuel Tweak | Additive fuel term | Increase/decrease additive term (offset) |
| 09 | Ignition Timing Offset | Adjust overall timing | Advance/retard timing (degrees) |
| 10 | Primary Fuel Tweak | Multiplicative fuel term | Increase/decrease multiplicative term (%) |
| 11 | Unused | Unused | |
| 12 | SEL Scaling (Turbo Cars Only) | Scale specified load | Increase/decrease requested boost (%) |
| 13 | Control Bits | Unused | |
| 14 | Idle Torque Additive Offset | Controls engine load at idle | Increase/decrease spec load at idle |
How lemmiwinks works
Directly transferring the new adaptation channel values into the ECU works by finding the RAM memory location where the ECU stores the adaptation channel data and directly writing the changes to those RAM memory locations. When the ignition key is turned off the ECU enters a housekeeping mode where among other tasks the modified adaptation channel data is written into the serial eeprom. This roundabout method is required because memory writes directly to the serial eeprom are blocked.
Interestingly, this method will not work using the VAG mode protocol. Write access is allowed to any ECU RAM location except those locations that store the serial eeprom data. Someone at Bosch clearly knew about this vulnerability and took measures to close this loophole. But for some reason this loophole was left in the KWP2000 routines.
Each ECU code stores this adaptation channel data in different RAM locations. To make this method work with any ECU one runs through the following steps:
- Establish communications with the ECU using KWP2000 mode
- Read data directly from serial eeprom (since read access is allowed)
- Search for this data in the ECU's RAM
- Write the new adaptation channel settings to the RAM location
- Cycle ignition key to have ECU transfer the new settings into the serial eeprom.
The KWP2000 protocol is not as reliable as the VAG protocol. Some cars will have communications problems which often can be worked around by pulling the instrument cluster fuse (make sure VAG-COM will be able to clear your air bag DTC light before doing this!).[1]